New NAT gateway IP addresses
We've added new NAT gateway IP addresses in the AWS US East (N. Virginia), US East (Ohio), and US West (Oregon) regions to expand infrastructure capacity. If you have IP allowlists on external systems that Neon connects to, update those allowlists to include the new addresses. Connections may be affected intermittently if traffic routes through non-allowlisted NAT gateways.
See our Regions documentation for the complete list of NAT gateway IPs for all regions.
New VPC endpoint services for Private Networking
We've added new VPC endpoint service addresses for Private Networking in the AWS US East (N. Virginia), US East (Ohio), and US West (Oregon) regions. If you've set up Private Networking in these regions, you can now use the additional endpoint service addresses for enhanced infrastructure capacity and reliability.
For the complete list of VPC endpoint service addresses by region, see our Private Networking guide.
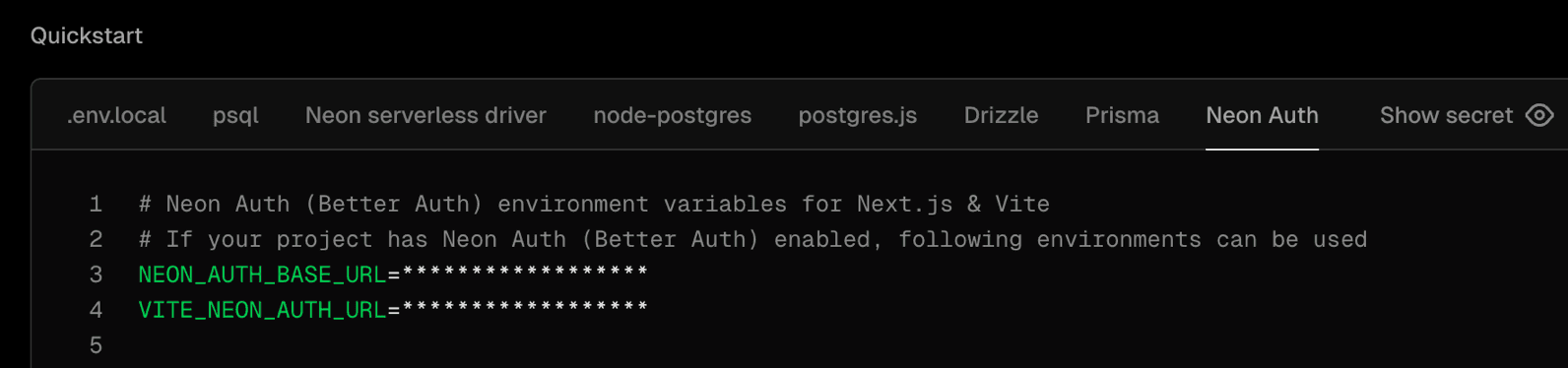
Neon Auth SDK simplified
We've released a major update to the server-side Neon Auth SDK (@neondatabase/auth/next/server) for Next.js applications.
Unified entry point
The SDK now uses a single createNeonAuth() function that replaces the previous separate functions (neonAuth(), authApiHandler(), neonAuthMiddleware(), createAuthServer()). Configure authentication once and access all functionality from a single object:
// lib/auth/server.ts
import { createNeonAuth } from '@neondatabase/auth/next/server';
export const auth = createNeonAuth({
baseUrl: process.env.NEON_AUTH_BASE_URL!,
cookies: { secret: process.env.NEON_AUTH_COOKIE_SECRET! },
});
// Use everywhere in your app
export const { GET, POST } = auth.handler(); // API routes
export default auth.middleware({ loginUrl: '...' }); // Middleware
const { data: session } = await auth.getSession(); // Server components
await auth.signIn.email({ email, password }); // Server actionsExplicit configuration
Configuration is now explicit rather than implicit. You must pass baseUrl and cookies.secret directly to createNeonAuth() instead of relying on automatic environment variable reading, making dependencies clear and eliminating "magic" behavior.
Session caching
Session data is now automatically cached in a signed cookie, reducing API calls to the Auth Server by 95-99%. Sessions are cached for 5 minutes by default (configurable) and automatically refresh as needed.
Breaking changes
This release includes breaking changes. If you're using Neon Auth and want to upgrade to the latest SDK version, you will need to update your application code. Key changes include replacing separate auth functions with the unified createNeonAuth() API, adding a required NEON_AUTH_COOKIE_SECRET environment variable, and adding dynamic = 'force-dynamic' to server components that use auth methods.
For detailed migration instructions, see the migration guide. For complete API documentation, see the Next.js Server SDK reference.
Getting started
To see the latest SDK in action, check out the demo applications, including a Next.js demo with server components, a React + Vite demo with external UI, and a React demo with the full neon-js SDK. The repository also includes AI coding assistant skills for Cursor and Claude Code with updated setup guides and code examples. See the Neon Auth quickstart guide and Server SDK reference to get started.
Neon Auth is a managed authentication service that branches with your database. See the Neon Auth overview to learn more.
Instagres adds REST API
Instagres now offers a REST API for programmatic database provisioning, making it easy to integrate Postgres into your platform, CI/CD pipelines, testing frameworks, and automation workflows.
The new API enables you to create databases with a single HTTP request:
curl -X POST https://instagres.com/api/v1/database \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{"ref": "your-app-name"}'The API returns a connection string, claim URL, and expiration timestamp. You can also retrieve database details using GET /api/v1/database/:id.
Instagres provides instant cloud-hosted Postgres that spins up in seconds. No signup or registration required. See the Instagres documentation for more information.
Data anonymization
- You can now anonymize columns that are part of primary keys when creating anonymized branches. Neon automatically handles foreign key constraints during the anonymization process, ensuring referential integrity is maintained across related tables.
Neon CLI
- The
neon initcommand now requires authentication before running. If you're not already authenticated, the CLI will automatically open your browser to log in. Additionally,neon initnow installs Cursor skills from the Neon skills repository instead of rules, providing more flexible and powerful AI agent capabilities for database development workflows.
To access these new features, upgrade to the latest version of the Neon CLI (version 2.20.2). For upgrade instructions, see Neon CLI upgrade.
Neon MCP Server
- The
provision_neon_authtool in the Neon MCP Server is now idempotent and returns your Neon Auth configuration details (base URL and JWKS URL) even when Neon Auth is already provisioned. This makes it easier to retrieve your authentication configuration without needing to make separate API calls.
Neon Skills
-
You can now install Neon agent skills as a Claude Code plugin, which bundles both the skills and the Neon MCP Server for natural language database management. See Neon Agent Skills.
/plugin marketplace add neondatabase/agent-skills /plugin install using-neon@neon-agent-skillsAgent Skills are resources that AI agents can discover and reference to help you work more accurately and efficiently with Neon.
Neon VS Code Extension
- The Neon VS Code Extension now automatically focuses on the Databases view after connecting to a branch, making it easier to immediately see your database schema and objects. The extension also includes performance improvements with smart caching and background data refresh for faster load times. Upgrade to the latest version to access these improvements.
OpenTelemetry integration
- The OpenTelemetry monitoring integration now supports gRPC protocol endpoints in addition to HTTP/HTTPS. When configuring an OpenTelemetry integration, you can use gRPC OTLP endpoints, and Neon will validate your credentials before saving the configuration.
SQL Editor
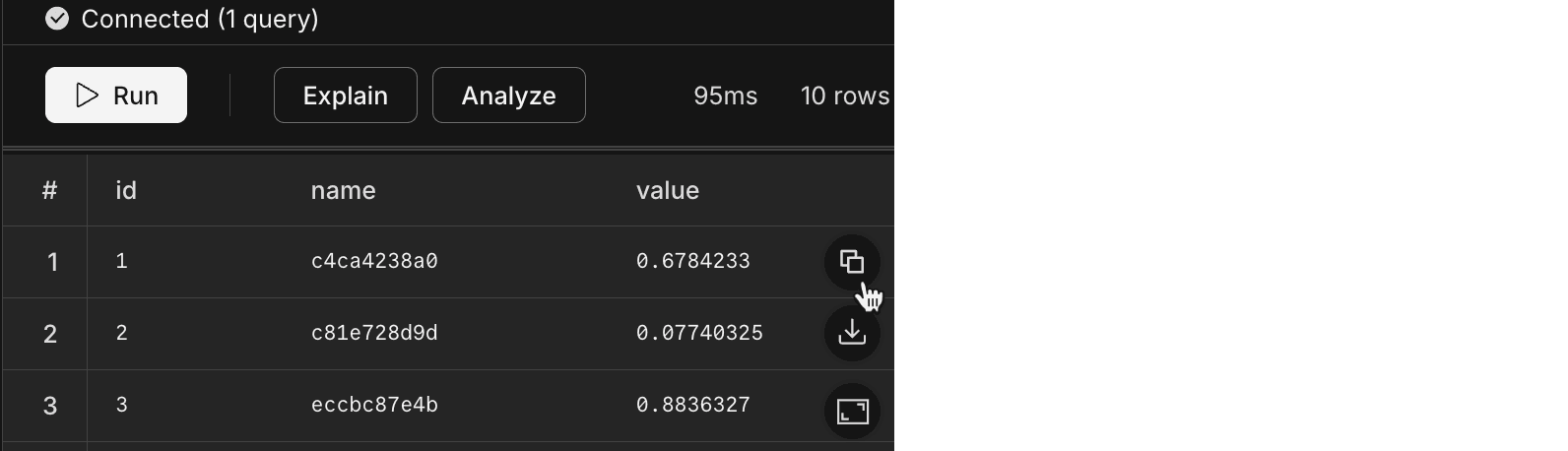
-
Added a copy button to the SQL Editor that lets you copy query results as JSON directly to your clipboard without downloading a file. The copy button appears alongside the download button in the query results view.
Fixes
-
Fixed an issue in the Neon consumption history API endpoint that caused errors when retrieving project consumption data.
-
Fixed an issue where deleting a Postgres role would fail if the role had been granted specific privileges (such as SELECT or INSERT) by another role. Role deletion now properly revokes all individual privileges before removing the role, ensuring successful deletion in all scenarios.